- PESTLE - Summary
Elements outside the company often have an impact on its future. To define a strategy, it is imperative to take into consideration what is happening in this environment. Changes in the world are increasingly rapid, can be more or less brutal and the company must constantly monitor this. This explains why strategies are set for shorter periods today than they were a few decades ago and can be redefined at any time.
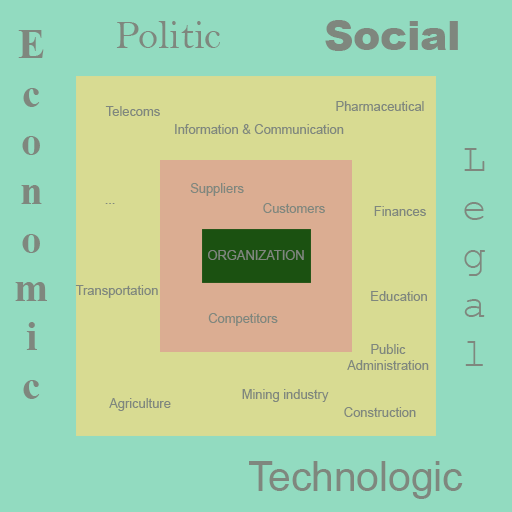
The company’s environment is composed of several layers. The closest environment is its market made up of its customers, its competitors, its suppliers and the regulations specific to the market. To study this stratum, the Porter Matrix is the most appropriate tool. Next comes the industry layer. For example, a cell phone operator is part of the telecom industry, as is an Internet service provider. And finally comes the 3rd layer, that of the macro-environment. It constitutes the most general environmental stratum that encompasses global factors that may be climate change, The Internet and new technologies, the aging of the population. All these effects have a more or less significant impact on the organization.
PESTLE criteria
The PESTLE criteria considered in the macro-environment are the following:
- Political
- Economical
- Social
- Technological
- Legal
- Environmental
PESTLE is a model that bears its name, it is the acronym of the variables that compose it. It allows for a breakdown of trends and potential problems for each of the variables. It should be noted that influences can be market or non-market.
We must then try to anticipate (with varying degrees of accuracy or certainty) the changes in the environmental variables likely to impact the organization, those listed with PESTLE.
At the end of this work, it will then be necessary to consider the scenarios of future developments (while remaining plausible). It is not about anticipating the future, that is the role of forecasting, but we will try to learn more about the possibilities of evolution of the environment.
- Observation
Still too few business leaders use this tool. The macro-environment is considered too vast, unpredictable and complex.
As a result, companies too often find themselves with their backs against the wall, have to undergo brutal changes in strategy or, more rarely, can get lucky by taking advantage of new opportunities.
However, luck is not the way to run a business. Imagine two farmers: one who will anticipate the weather during the week and plan his work, and the other who will notice the weather situation every morning and adapt. Which one do you think will perform better? In every industry, it is anticipation and planning that has allowed us to seize opportunities or ward off threats.
- Why use PESTLE tool?
- Analyze the macro-environmental factors that impact the company.
- Anticipate potential threats that may impact the company.
- Anticipate potential opportunities that may arise in the near to distant future.
- Set up scenarios for the future, in order to make the right decisions today.
- Market and non-market dimensions of the PESTLE model
- Market dimension (economic relationship)
- Clients
- Suppliers
- Competitors
- Non-market dimension (but can be influenced by economic factors)
- Social factors
- Legal factors
- Political factors
- Ecological factors
- In the non-market environment, companies must :
- build their reputation, their image,
- be able to influence,
- be legitimized.
Lobbying is developing, networks are being created, communication services are emerging, and there is also talk of the impact of CSR policy. If the company resorts to subsidies or donations, these factors are very important (hospitals, schools, associations…). If the influence of regulators or public authorities is decisive, these factors are key.
For organizations in smaller countries, the role of the state is generally strong and politics, media and business are closely linked. These factors are also very important.
- Market dimension (economic relationship)
Political factors
These PESTLE political factors correspond to the impacts linked to the decisions of governments and institutions. In the country in which the organization operates, but also in a country in which a subsidiary, a supplier or even customers are located. At this level, we analyze for example:
- the stability of the political system, the parties in power, their orientations, the possible changes that could occur in future elections
- social protection,
- taxation,
- foreign trade policy,
- subsidy or aid schemes for businesses,
- the rate of corruption,
- lobbies,
- the degree of freedom of the press,
- …
These are the PESTLE economic influencing factors. You have to look at the economic dynamism, the purchasing power, the consumer behavior, the ability to borrow money. In particular, the following elements should be analyzed:
- economic growth, GDP and/or GNP
- disposable income, purchasing power,
- the unemployment rate,
- the inflation rate,
- economic stability,
- interest rates,
- access to finance
- access to skills (human resources),
- …
A lot of information is available with INSEE’s tools and databases.
Economical factors
Social factors
These are demographic factors. We study the characteristics of the population and its behavior (attitudes, values, norms…). Here are some examples to consider in PESTLE:
- how income is distributed,
- demography (study of populations),
- social mobility,
- educational attainment,
- attitudes towards leisure and work,
- …
Here we are interested in the factors related to technology. For any company, the evolution of technologies can represent threats or opportunities. Here are some examples of elements that can be taken into consideration:
- the level of innovation for a technology,
- potential disruptive technologies,
- access to new technologies,
- the development of communication and distribution channels,
- …
In the field of technology, the company must anticipate to seize potential opportunities. If it remains passive in the face of innovations, the company will sooner or later be threatened with losing its customers (new uses to which the company does not know how to respond) or will be overtaken by its competitors who will have been able to react in time.
Technological factors
Environmental factors
Environmental factors should also be taken into consideration. Some examples for PESTLE:
- environmental protection laws and regulations,
- waste reprocessing,
- regulations in terms of pollutant emissions,
- recycling standards,
- availability of natural resources,
- …
These factors have become increasingly important in recent years, and the trend will grow in the future, given the evolution of pollution in the world. Companies with an industrial activity must be particularly vigilant in this area (waste treatment, energy consumption, etc.). The environmental factor can be a real asset for a company particularly sensitive to ecology.
Finally, the legal factors concern the legislation applicable in the country or countries with which the company works. Here are some examples of elements to analyze:
- competition law,
- intellectual property law and protection (copyright, patents, trademarks…).
- health law,
- labor law,
- business law,
- worker’s rights,
- consumer law,
- data protection law,
- …
This last component is very important, because the company must respect the legal framework applicable to it. For example, for a company that develops a digital activity, taking into account the RGPD (General Data Protection Regulation) is very important.
Legal factors
PESTLE allows you to understand and analyze the evolution of the environment in 5 areas that can have an impact on the company. Set up a global reflection with the right stakeholders, those who can really help you and who have a good mastery of the topics addressed.
Benchmarking can be helpful in finding solutions. And, of course, it is essential to compare your vision with other members of the company.
Project manager since 1998, Agile since 2001 then PMO since 2009, I accompany companies in the realization of their projects/programs, in the construction and management of the PMO, in the improvement of processes and I help managers to improve their performance.
Related
Articles non similaires.